From Limping to Diagnosis: Helping Pets Improve Their Mobility
A limp may start subtly, but over time it can affect your pet’s ability to play, exercise, or even rest comfortably. Causes range from soft tissue injuries to arthritis, fractures, or systemic disease. Diagnostic imaging and lab testing help determine what’s minor and what needs immediate attention.
At Memorial Villages Animal Hospital in Houston, TX, advanced services such as laser therapy, acupuncture, and rehabilitation help pets regain comfort and mobility while addressing the root cause.
Understanding Limping in Pets: Causes and Concerns
When your dog or cat begins favoring one leg or walking with an uneven gait, the cause may be as simple as a muscle strain or as serious as a fracture or ligament tear. Knowing what to look for helps you decide when to rest your pet and when to seek care.
Common Causes of Limping
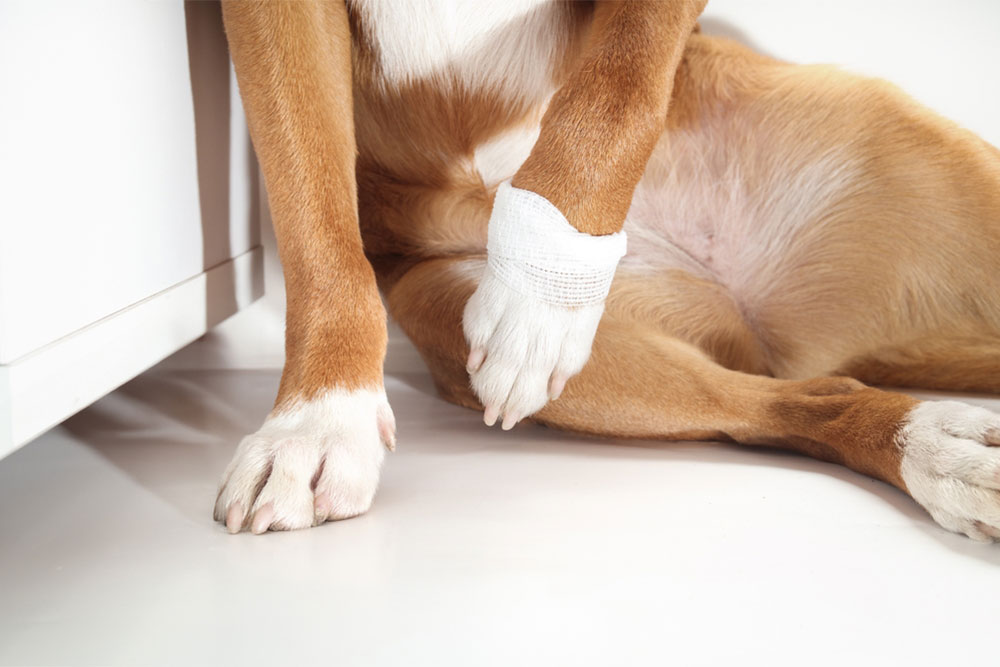
- Injuries and trauma: Sprains and strains often resolve with rest and anti-inflammatories. More serious injuries, including broken bones, may require surgery. Falls, vehicle accidents, and rough play can cause fractures that aren’t always visible. Cruciate ligament injuries are one of the most common injuries, most often in large dogs. Even something as minor as a torn toenail injury can cause a limp.
- Joint and bone disorders: Arthritis causes stiffness and pain, often worse after rest. Large dogs may develop hip dysplasia, while patellar luxation is more common in small breeds and cats. Immune-mediated polyarthropathy can cause pain in multiple joints.
- Infection or inflammation: Bite wounds or embedded debris can introduce bacteria into soft tissue or bone. Rapidly growing dogs sometimes develop panosteitis, which causes shifting leg pain.
- Foreign bodies: Foxtails, thorns, or glass can lodge in the paw, leading to sudden limping and swelling until removed.
Why Prompt Action Matters
Addressing lameness early prevents chronic pain and compensatory injuries. A simple strain can worsen if left untreated as your pet shifts weight to the opposite limb. Recognizing common pain signs– such as hesitation with stairs, slower walks, or reluctance to play- can help you seek care before limping becomes severe.
Diagnostic Tools: Identifying the Cause
Pinpointing the source of limping involves a hands-on exam, your observations, and targeted diagnostics. This combination differentiates conditions that look similar but require very different treatments.
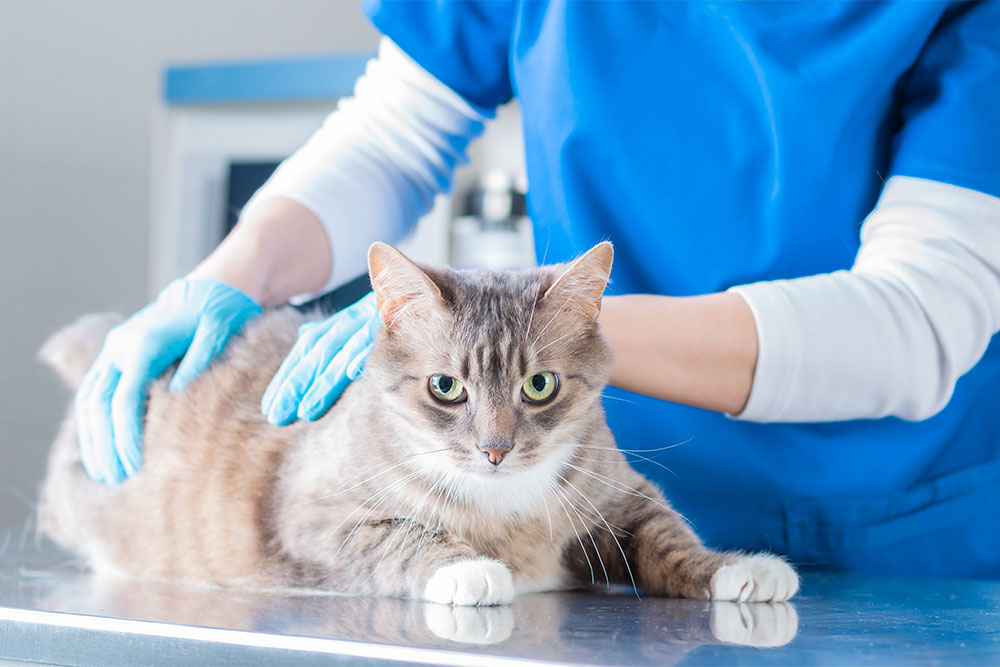
Physical Exam and Health History
At Memorial Villages Animal Hospital, our veterinarians observe gait, assess range of motion, and palpate joints and muscles for pain or swelling. We’ll ask when the limping began, what makes it better or worse, and whether your pet recently exercised, jumped, or played roughly. Details about age, breed, and previous injuries help us narrow the cause quickly.
Advanced Imaging and Testing
When a physical exam isn’t conclusive, digital imaging provides clarity. X-rays reveal fractures, arthritis, or joint abnormalities, while ultrasound assesses tendons, ligaments, and fluid accumulation.
For complex cases, CT scans and MRI visualize deeper structures like cartilage or nerves. Bloodwork may reveal infection, immune-mediated disease, or metabolic disorders affecting mobility. Biopsies are performed when tumors or unusual lesions are found.
Treatment Options: From Pain Relief to Rehabilitation
Successful treatment addresses both the immediate pain and the root cause. Depending on your pet’s diagnosis, your veterinarian may recommend medication, surgery, rehabilitation, or a combination of therapies.
Immediate Care and Pain Management
Anti-inflammatories, rest, and pain relief help most pets early in recovery, improving comfort and reducing inflammation. As activity resumes, structured warm-ups and cooldowns and gradual increases in exercise prevent re-injury and maintain flexibility.
Surgical Interventions
Some orthopedic conditions- like cruciate ligament tears, severe hip dysplasia, or complex fractures- require surgery. Modern techniques can restore stability and motion, especially when addressed promptly. Postoperative rehabilitation is essential to rebuild strength and prevent secondary strain.
Alternative Therapies
Integrative care enhances recovery and reduces long-term medication needs.
- Acupuncture and chiropractic care improve circulation, relieve inflammation, and restore mobility for pets with arthritis or chronic pain.
- Regenerative medicine treatments such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell therapy use the body’s healing mechanisms to repair damaged tissue. Regenerative therapies for pets have been shown to reduce inflammation and support lasting joint health.
- Cold laser therapy promotes cell repair and circulation, accelerating healing after injury or surgery. Laser therapy for pets offers gentle, repeatable pain control- ideal for older pets or those with chronic arthritis.
The Importance of Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation bridges the gap between medical treatment and full recovery. It helps restore strength, coordination, and mobility while reducing pain and stiffness. For pets recovering from injury, surgery, or chronic orthopedic disease, a structured rehab program can make the difference between partial and complete recovery.
Rehabilitation therapies for animals are tailored to each patient’s needs and may include therapeutic exercises, underwater treadmill sessions, massage, stretching, and balance training. These methods improve circulation, rebuild muscle mass, and encourage proper joint movement.
By combining these treatment modalities, veterinarians can design individualized plans that relieve pain, support healing, and improve long-term mobility.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
A proactive plan helps prevent recurrence and keeps your pet active and comfortable.
Routine Veterinary Checkups
Regular wellness visits detect problems before they escalate. Annual or semiannual exams help monitor joint function, body weight, and early signs of disease.
Lifestyle and Home Adjustments
- Keep pets at a healthy weight to minimize joint stress.
- Provide joint-supportive nutrition, including omega-3s or glucosamine as advised by your veterinarian.
- Limit slippery floors, reduce high jumps, and use ramps or pet stairs when needed.
- Maintain nail and paw care to prevent slips or torn and broken nails
Myths About Limping
- “It will just go away.” Hoping a limp resolves on its own often leads to worsening pain or secondary injuries. Early evaluation protects long-term function.
- “It’s just old age.” Aging isn’t a diagnosis. Senior pets benefit from pain management, joint supplements, and therapies that restore comfort and confidence.
Reliable information and veterinary guidance help owners make informed decisions based on facts, not assumptions.
When to Seek Veterinary Help
Some limps improve with rest; others deteriorate quickly. Knowing when to act prevents unnecessary pain.
Recognizing Emergencies
Seek immediate care for severe pain, non-weight-bearing lameness, open wounds, or visible deformity. Fever, lethargy, or systemic illness combined with limping are also urgent signs. Memorial Villages Animal Hospital provides emergency and urgent care during business hours. Call ahead to contact our team so we can prepare for your arrival.
Follow-Up and Ongoing Care
For mild limps that persist beyond 48 hours, schedule an appointment to determine the cause and prevent complications. Follow-ups allow your veterinarian to adjust medications, rehabilitation exercises, and activity as healing progresses. Most pets recover best with several weeks of guided care and gradual conditioning.

Your Pet’s Path to Pain-Free Movement
Limping rarely resolves fully without addressing its cause. Early diagnosis and treatment lead to faster recovery and better long-term results.
If your pet shows persistent limping, stiffness, or reluctance to move, call Memorial Villages Animal Hospital at (346) 472-3004 or book an appointment online. Our team will find the source of your pet’s pain, provide effective treatment, and help restore the active, comfortable life they deserve.








Leave A Comment